Regular backups are crucial for any production database. In this article, I’ll show you how to automate PostgreSQL dumps using a Python service deployed on Google Cloud Run, triggered by Cloud Scheduler.
Project Overview
This project provides a Python Flask application that performs PostgreSQL dumps and uploads them to Google Cloud Storage. The service is designed to run serverlessly on Cloud Run and can be triggered on a schedule using Cloud Scheduler.
Key Features
- Secure password retrieval from Secret Manager
- Flexible schema/table inclusion and exclusion
- Automated upload to Google Cloud Storage
- Easily triggered by Cloud Scheduler
Prerequisites
Before deploying, make sure you have:
- A Google Cloud Storage (GCS) bucket: This is where your database dumps will be stored.
- A service account: This account must have the necessary permissions to write to your GCS bucket (roles/storage.objectUser) and to get the user password in Secret Manager (roles/secretmanager.secretAccessor) The service account should be assigned to your Cloud Run service.
How It Works
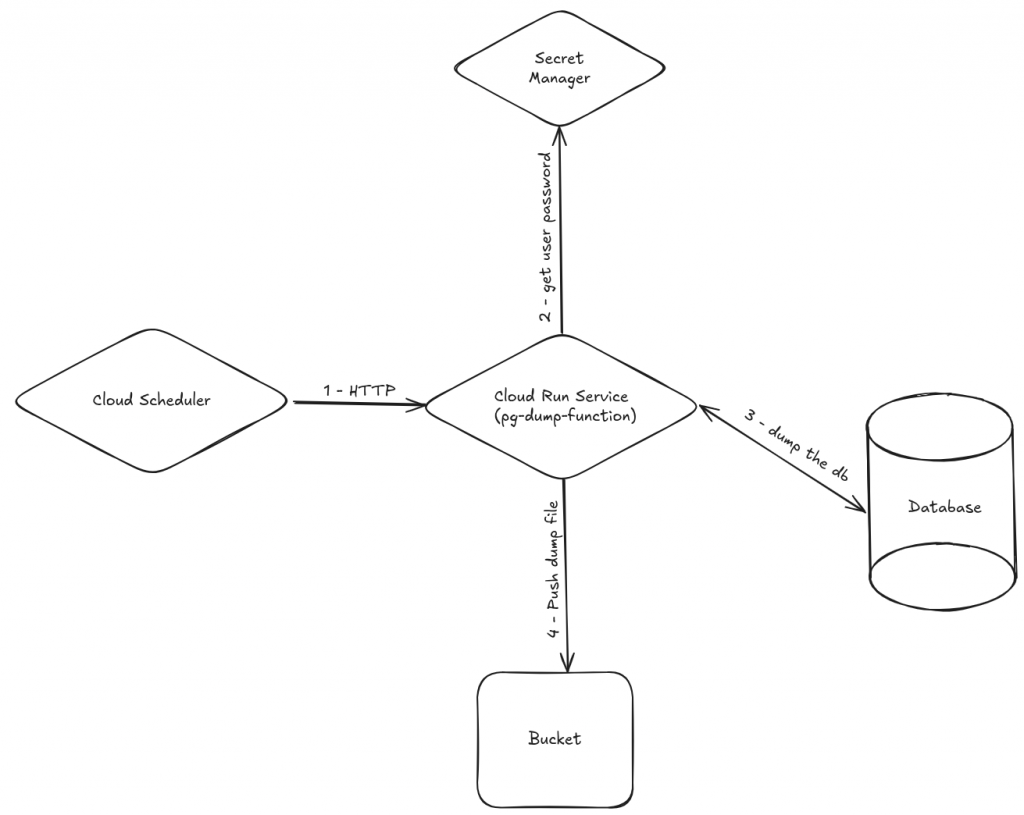
- Cloud Scheduler triggers the Cloud Run service via HTTP.
- Cloud Run service connects to Secret manager to retrieve the user password use by pg_dump.
- Cloud Run service connects to your Cloud SQL instance using the Cloud SQL Auth proxy.
- It runs
pg_dumpwith customizable options (schemas/tables to include or exclude). - The dump file is uploaded to your GCS bucket.
Step-by-Step Setup
1. Deploy to Cloud Run
Deploy your image to Cloud Run (replace variables with your values):
gcloud run deploy pg-dump-function \
--image=docker.io/damsdgn29/pg-dump-function:latest \
--region=YOUR_REGION \
--service-account=YOUR_SERVICE_ACCOUNT \
--set-env-vars="GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT=YOUR_PROJECT" \
--set-env-vars="REGION=YOUR_REGION" \
--set-env-vars="DB_INSTANCE_NAME=YOUR_INSTANCE" \
--set-env-vars="DB_NAME=YOUR_DB,DB_USER=YOUR_USER" \
--set-env-vars="SECRET_NAME=YOUR_SECRET" \
--set-env-vars="GCS_BUCKET=YOUR_BUCKET"You can also set optional environment variables to customize your dumps:
INCLUDED_SCHEMAS,EXCLUDED_SCHEMASINCLUDED_TABLES,EXCLUDED_TABLESDUMP_BASE_NAME
Example:
--set-env-vars="INCLUDED_SCHEMAS=public,EXCLUDED_TABLES=logs"2. Configure Cloud Scheduler
Create a Cloud Scheduler job to trigger the Cloud Run service at your desired frequency:
gcloud scheduler jobs create http pg-dump-schedule \
--schedule="0 2 * * *" \
--uri="https://YOUR_CLOUD_RUN_URL" \
--http-method=POST \
--oidc-service-account-email=YOUR_SERVICE_ACCOUNTThis will trigger your Cloud Run service every day at 2 AM.
Customizing Your Dumps
The service supports flexible inclusion and exclusion of schemas and tables via environment variables. For example, to exclude the logs table and only include the public schema, set:
INCLUDED_SCHEMAS=publicEXCLUDED_TABLES=logs
Conclusion
With this setup, your PostgreSQL backups are automated, secure, and stored in Google Cloud Storage. Cloud Run provides scalability and reliability, while Cloud Scheduler ensures regular execution. Make sure your service account has access to your GCS bucket for successful uploads.
Check out the GitHub repository for more details and to get started!
